
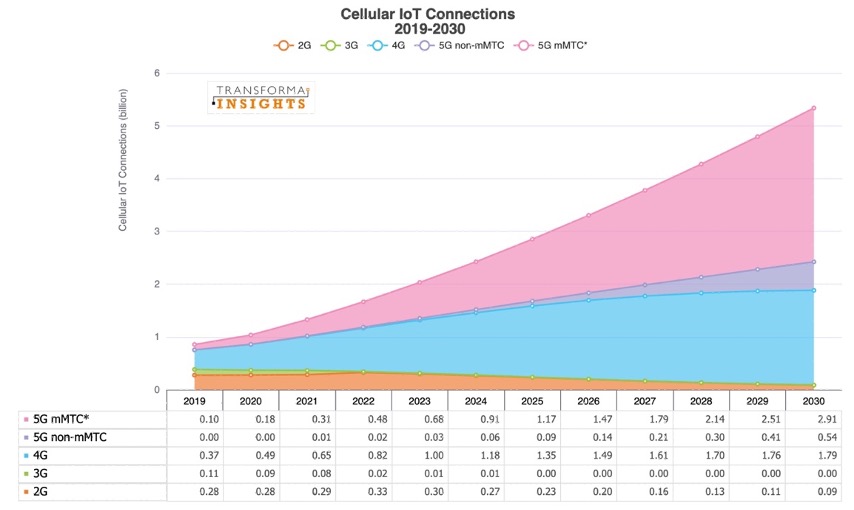
The number of connected IoT devices is thriving and IoT connections research from Transforma Insights predicts 5 billion cellular IoT connections by 2030. 5G massive machine-type communication (mMTC), developed to complement earlier MTC technologies such as NB-IoT or LTE-M and 4G, will become the default cellular technology. Low-cost battery-powered devices are predicted to be a key market segment of connected IoT devices. eSIM is an enabler for cellular IoT device connectivity, which allows them to be provisioned remotely over the air and store multiple sets of mobile network operator credentials. In other words, IoT devices benefit from future technology upgrades and often cheaper data charges.
The global deployment of cellular-connected IoT devices with embedded SIM (eSIM) can be complex. This is due to regional variations in cellular coverage, wireless technology, and roaming regulations. As a result, original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) developing IoT and M2M solutions and the enterprises deploying these devices must carefully consider their connectivity requirements.
“eSIM is an enabler for connected cellular IoT devices, which allows them to be provisioned remotely over the air and store multiple sets of mobile network operator credentials.”
-Kigen UK Limited
Reliable Connections & Trusted Data
IoT devices use sensors to collect information and monitor environmental changes. The data is subsequently transmitted for analysis to inform business decision-making. Hence, IoT applications need a reliable connection to gather trusted operational and transactional data.
Cellular networks operate by implementing global industry standards and are managed by wireless network providers. It is essential that the network provider and in certain cases, the IoT service provider, deliver reliable security measures such as those described in the GSMA IoT security guidelines for operators.
Why Use eSIM
OEMs design connectivity into their products at the development stage to best suit their requirements. Consequently, selecting and designing the appropriate connectivity module in development ensures a device’s cellular operation.
The choice of SIM support is also critical, as using an embedded form factor with eSIM capability delivers significant benefits, including remotely enabling local carrier connectivity in the field. Also, the manufacturing costs for OEMs are more manageable as they have a single stock-keeping unit (SKU) with more control of in-life connectivity.
Benefits of eSIM
There are several specific benefits to note:
- eSIM delivers the capability to remotely change a device’s connectivity provider with the ability to deploy a local connectivity profile and avoid regulatory-prohibited permanent roaming.
- Deploying alternative profiles to change Cellular Carriers can improve available coverage or utilize the most economical tariff.
- An eSIM can be employed in cellular devices supporting a variety of radio technologies from 2G through to 5G, including NB-IoT, LTE-M, and 5G REDCAP.
- eSIMs uphold tamper-proof, robust security and offer trusted end-point network subscriber identity management.
- eSIM profiles for machine-to-machine devices can be quickly and securely managed remotely through a centralized platform based on GSMA eSIM standardized specification.
Choosing a Mobile Network Operator
Cellular radio technology deployments and related geographic coverage vary between carriers and from country to country. Device manufacturers and deploying enterprises must consider these variants when designing their devices or planning the support for their device usage.
The integrated connectivity technology must support the expected deployment regions, data requirements, the types of devices, and their power constraints. This is especially critical for transient things installed in objects such as haulage vehicles, shipping containers, or pallets.
This ability to quickly and frequently cross-country borders makes eSIM and remote profile management a key feature to evaluate for inclusion in these use cases.
Connectivity Challenges for IoT Devices
IoT traffic content and volume can vary based on the device type and its use, with the number of active devices and anticipated service consumption influencing subscription tariff economies. For instance, some low-powered static devices, such as smart meters, won’t always generate data or be online but will typically use services from the same network.
On the other hand, logistics tracking devices that are constantly moving will dip in and out of coverage and often travel from one country to the next. These rely on roaming to change networks and maintain connection, incurring increased charges.
Some regions insist on using local carriers as they don’t allow permanent roaming for IoT devices. The expectation is that global roaming works seamlessly for devices produced in one country and deployed in multiple regions.
Enterprise Considerations
The following should be taken into consideration:
- Poor coverage in certain regions
- MNO subscription lock-in
- Roaming restrictions and high tariffs. Regulations in some countries prevent term term-long-term
roaming, with which switching to local MNO is a must to maintain connectivity. - The complexity of managing multiple network operators with different regulations
- Lack of MVNOs with roaming agreements to support multi-national IoT requirements
- Quality of Service needed by the IoT application
- Lack of flexibility in the business model as needed by the IoT application
Tweet
Share
Share
- 5G
- Cellular
- Connectivity
- eSIM
- NB-IoT
- 5G
- Cellular
- Connectivity
- eSIM
- NB-IoT
